Both Sage and SAP offer human capital management (HCM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) solutions for businesses looking to manage a large workforce. While Sage and SAP do offer many of the same features, they don’t completely overlap.
Sage and SAP are designed with different size businesses in mind: Sage is geared more toward midsize and large businesses, whereas SAP is better suited for enterprises due to its complexity.
In this Sage versus SAP comparison, we delve into the similarities and differences between the two platforms.
Jump to:
| Features | Sage | SAP |
|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Contact sales for quote | Contact sales for quote |
| Payroll | Yes | Yes |
| Human capital management | Yes | Yes |
| Financial management | Yes | Yes |
| Workforce management | Yes | Yes |
| CRM | Yes | Yes |
| Operations management | Yes | Yes |
| Try Sage | Try SAP |
While Sage discloses pricing for its small-business accounting software, it doesn’t disclose pricing for its HCM and ERP software, which is geared towards medium and large businesses and thus a more direct comparison to SAP. You must contact the Sage sales team for a custom pricing quote based on the exact features you need.
Sage doesn’t offer a free trial for these more advanced plans.
The SAP website is a bit more transparent. The SuccessFactors HCM software package starts at $6.30 per user per month, but that’s about all we learn. So to get a more accurate quote, you’ll have to get in touch with SAP.
Also, like Sage’s HCM and ERP software, SAP SuccessFactors doesn’t have a free trial.
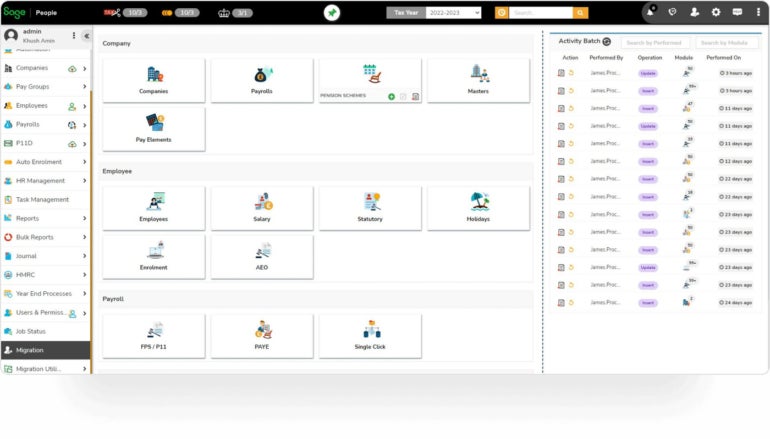
Sage’s payroll system (Figure A) is powered by ADP, which is one of the global leaders in payroll software. The payroll system automates manual calculations such as taxes and the number of hours worked. This helps your company protect against tax-filing errors and stay compliant with federal, state and local laws. Once you’ve checked all the alerts to confirm accuracy, you can quickly run payroll and pay your employees.
Figure A
SAP includes payroll as part of its core HR package. Companies can pay employees in more than 100 countries using the platform, which is designed to be used with in-house, outsourced and hybrid payroll models. The system incorporates local requirements such as labor laws to keep your company compliant. Alerts proactively notify your team of errors so they can be corrected before payroll is run.
Sage includes many HCM features, including recruiting software, benefits administration and performance management. It also offers an employee engagement module, called Workforce Experience Management. However, it doesn’t have a learning management system, which sets it apart from SAP.
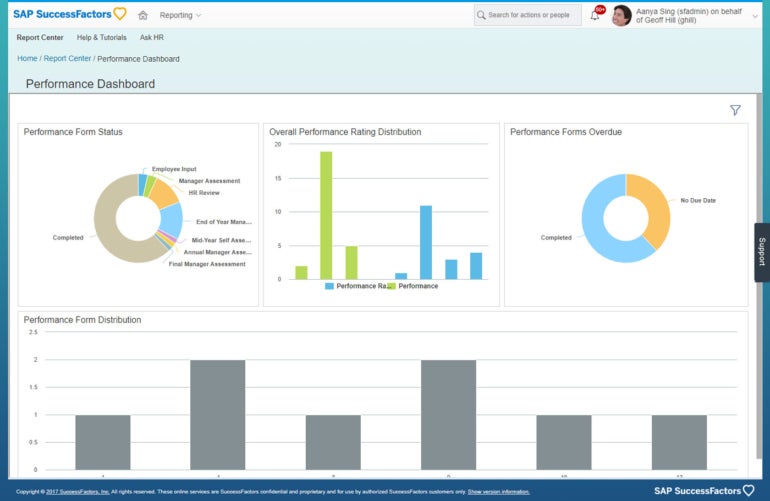
SAP’s HCM package includes almost every fundamental module. You can find qualified candidates with the recruiting software, manage open enrollment with benefits administration and track goals with the performance management software (Figure B). You can also gather feedback with the employee engagement bundle and help employees prepare for the future with the learning management system.
Figure B
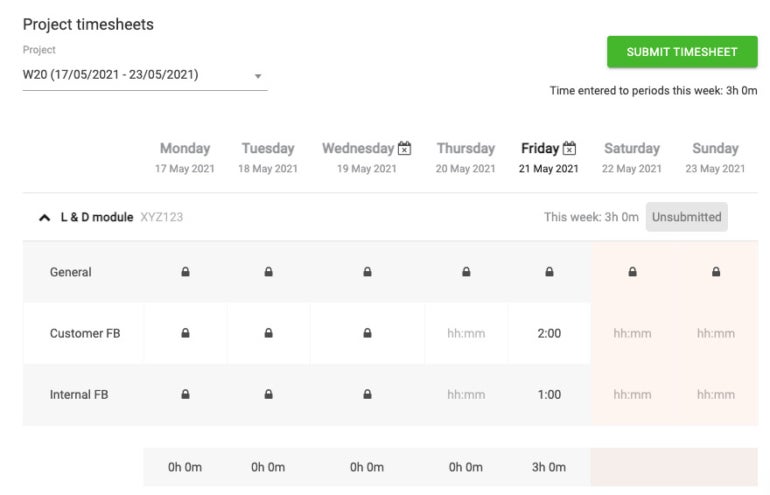
Sage includes a module for timesheets (Figure C) so employees can clock in and out to track their time. It also has a scheduling tool to help your company forecast labor requirements and create schedules based on employee availability. This helps to increase staff productivity and reduce administrative time, resulting in cost savings.
Figure C
SAP’s workforce management products are included as parts of its HCM software. With SAP, you can create fully optimized schedules for your entire organization and forecast your labor requirements ahead of time. Employees can clock in or out using web, mobile or external clocks, and the data can be integrated directly into the payroll solution.
Sage is known for its intuitive cloud accounting software, which is incorporated into its financial management software. Sage automates complex processes and delivers real-time reporting to support strategic decision making. It also includes tools for spend and budget management to help limit overspending and unexpected costs.
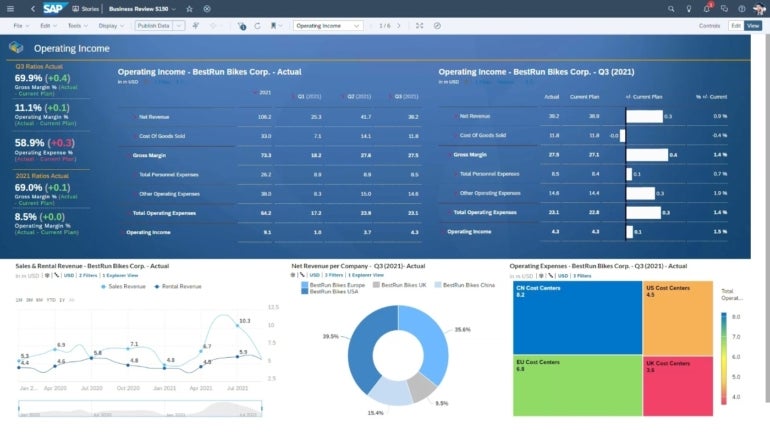
In addition to payroll, SAP also includes tools for financial management, spend management and accounting. Manual processes and calculations are automated to reduce work and mistakes. Centralized reporting (Figure D) creates a single source of truth and delivers analytic insights to help company leaders make data-driven decisions.
Figure D
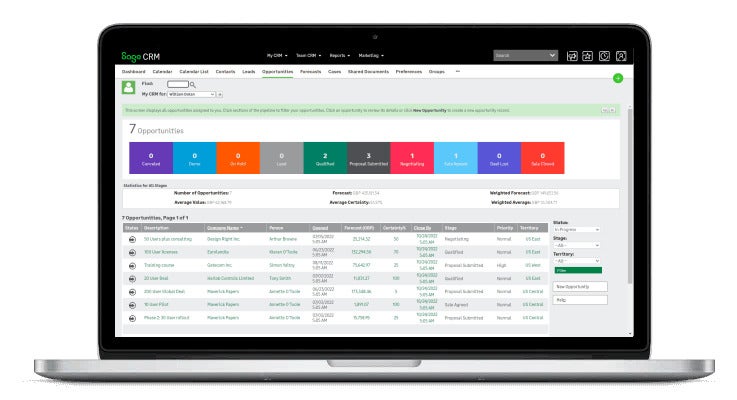
Sage offers both a fully integrated CRM (Figure E) and a la carte Sage Sales, Marketing and Service modules so that you can choose the plan that makes the most sense for your business needs. The CRM automates sales tasks like creating quotes and orders and also helps your sales team pursue leads and convert them to paying customers.
Figure E
If you don’t already have a CRM, SAP offers its own CRM and customer experience solutions. You can explore customer data, create personalized experiences and optimize marketing interactions through the platform.
Sage offers supply chain management and operations management software to create one centralized source of information. You can communicate with suppliers, fulfill orders accurately and quickly, manage warehouse inventory and more within the Sage system.
SAP also includes tools for SCM and inventory management. You can track goods receipts, goods issues and the internal movement of materials to manage your inventory. The SCM product integrates with the rest of SAP so that you can contextualize your supply chain and see how it will affect the rest of your business.
When researching these ERP planning software solutions, we took a look at a number of sources, including product documentation, demos and videos, and consulted user reviews. We also dug into features such as payroll, accounting, human capital management, financial management, workforce management, CRM and operations management. And we weighed factors such as the user interface and experience, customer support and security.
As you can see, both Sage and SAP offer a similar set of enterprise resource planning features, though there are some key differences. SAP offers a learning management system and Sage doesn’t. Sage’s payroll is also powered by ADP, and SAP has a native payroll platform that doesn’t involve third-party partners.
While SAP does try to market itself to smaller businesses, users say that the complexity of the software makes it better suited to enterprises. Meanwhile, Sage is geared to small and medium businesses and offers two tiers of pricing plans for businesses of each size.
Neither Sage nor SAP offers a free trial, so we recommend researching ahead of time so you can come to the sales demo call prepared with specific questions. Check out comparisons of SAP vs. Oracle and SAP vs. Workday to discover how it stacks up against other popular ERP software.
Rippling is the first way for businesses to manage all of their HR, IT, and Finance — payroll, benefits, computers, apps, corporate cards, expenses, and more — in one unified workforce platform. By connecting every business system to one source of truth for employee data, businesses can automate all of the manual work they normally need to do to make employee changes.