
Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm are data science notebook and development tools, respectively. Compare key features to see which tool is best for your business.
Choosing the right integrated development environment or data science notebook solution is key to increasing productivity and streamlining the research or development process for maximum efficiency. Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm are two popular choices that offer their own specific benefits in different areas of data science and software development.
SEE: Take advantage of TechRepublic Premium’s data engineer hiring kit.
Jump to:
Jupyter is a browser-based, open-source data science notebook tool that supports Python, Julia, and other dynamic programming languages such as R, Scilab and Octane. Focused on scripts and accompanying documentation, Jupyter is ideal for data scientists who need a way to create quick data visualizations. However, source code is stored as HTML and readable by Jupyter rather than Python.

PyCharm is a dedicated IDE tool focused on providing a complete solution for creating full-fledged packages and software in Python, including classes and graphical user interfaces. It also excels in complex environments where multiple scripts interact with each other and need to be managed.
PyCharm’s most popular features include a built-in debugger and smart autocomplete, as well as DevOps tools such as version control, which makes it ideal for developers and software engineers.
Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm have distinct features, which make each of these data science tools better for specific applications. For instance, Jupyter’s features are more suited to data analysts and research applications, whereas PyCharm’s features are designed for developers and software engineering.
| Features | Jupyter Notebook | PyCharm |
|---|---|---|
| Smart auto-complete | No | Yes |
| Inline code execution using blocks | Yes | No |
| Single line graphing support | Yes | No |
| Intelligent code analysis | No | Yes |
| Integration with popular tools | Yes | Yes |
| Starting price | Free | $249 per user, billed annually |
Jupyter Notebook offers a 100% open-source solution released under the liberal terms of the modified BSD license. It is free to access and use, making it an excellent option for companies seeking to economize on software expenses.
By comparison, organizations must pay to use PyCharm. The solution starts at $249.00 per user for the first year of use. The price then falls to $199.00 per user during the second year and finally to $149.00 for the third year and onwards.
Both Jupyter and PyCharm allow you to execute your code in place and offer ways to analyze or determine where errors are originating. That said, Jupyter is more flexible in this regard, as it allows for single line executions, which saves time in finding coding errors and makes the platform ideal for trial-and-error coding or experimentation (Figure A).
Figure A
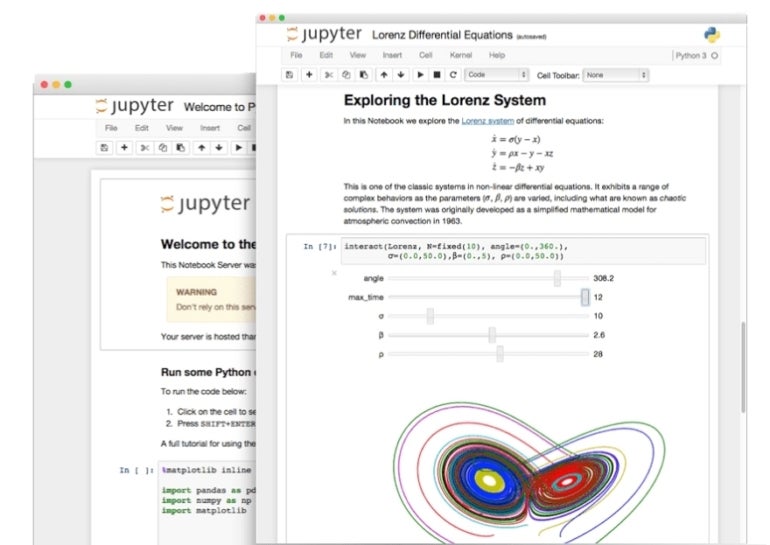
With PyCharm, you would need to complete or change the entire snippet of code in order to run it and observe the output. As a result, testing or experimenting with code is slower, and finding coding errors is a much more meticulous task compared to Jupyter.
PyCharm’s autocomplete feature really facilitates faster development and workflow, and it is something that Jupyter does not offer (Figure B). This smart editing feature is why PyCharm is clearly the choice for developers and software engineers, especially those working exclusively in Python.
Figure B
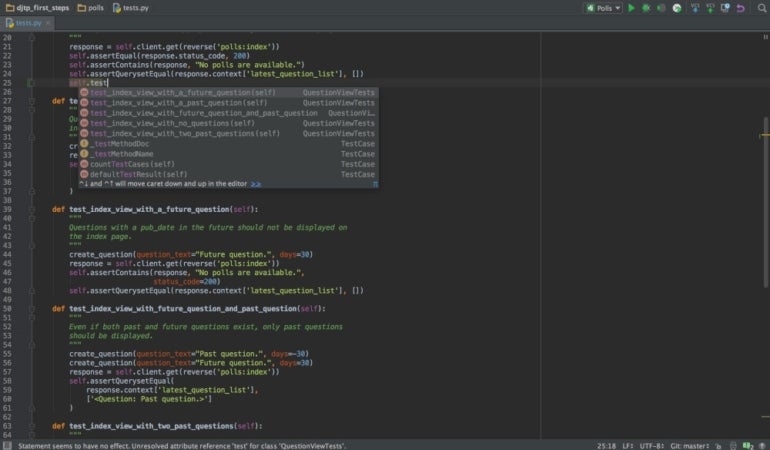
Jupyter has unique coding features as well, but they are mostly aimed at visualization. This includes the ability to graph or visualize individual lines of code or data, which is something PyCharm does not offer. This is a handy tool for data science or research applications, where the intended audience of the output is non-technical.
Both of these tools offer a host of built-in integrations for frameworks and other developer productivity tools. Although they share some of the same integrations, there are some tools that are not shared.
Some key integrations for Jupyter that PyCharm does not offer are GitHub, Dropbox, Scala and TensorFlow. PyCharm offers integration with Django, Kite, Wakatime and Pytest.
This is a technical review using compiled literature researched from relevant databases. The information provided within this article is gathered from vendor websites or based on an aggregate of user feedback to ensure a high-quality review.
When considering an integrated development environment, the decision is often based on personal preference as well as the platforms’ respective applications.
Jupyter is more of a data science notebook, and the tools and features are geared to research or data science projects that require sharing and visualizing data. The ability to graph inline as well as add text, HTML and other features alongside the code all work towards this goal.
PyCharm is aimed at developers looking to make complex software, complete with GUIs and other features. The smart editing, intelligence analysis and auto completion all are geared towards streamlined developer efficiency. PyCharm also has much-needed features for developers like version control, safe refactoring and other tools.
Domo puts data to work for everyone so they can multiply their impact on the business. Underpinned by a secure data foundation, our cloud-native data experience platform makes data visible and actionable with user-friendly dashboards and apps. Domo helps companies optimize critical business processes at scale and in record time to spark bold curiosity that powers exponential business results.
Wyn Enterprise is a scalable embedded business intelligence platform without hidden costs. It provides BI reporting, interactive dashboards, alerts and notifications, localization, multitenancy, & white-labeling in any internal or commercial app. Built for self-service BI, Wyn offers limitless visual data exploration, creating a data-driven mindset for the everyday user. Wyn’s scalable, server-based licensing model allows room for your business to grow without user fees or limits on data size.