At first glance, PBX and VoIP seem like two very different types of phone systems. But modern technology, like IP PBX, cloud PBX, and SIP gateways, allows many businesses to use a combination of both.
The variety of options and combinations means you will be able to create a custom phone system that matches your needs — and you likely won’t have to worry about the differences between PBX and VoIP during your search for a new phone system. Any provider worth considering should be able to help you navigate your options with ease.
PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is a traditional telephone system that operates on analog lines. It allows internal communication within an organization and connects calls to the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network).
Essentially, this lets your calls travel over physical wires to connect you with the person on the other line.
In the past, these systems needed human operators to plug and unplug cables — businesses had to employ a lot of them to keep operations running smoothly.
Then came PABX (Private Automatic Branch Exchange). This automated the manual aspects of connecting calls, eliminating the need for human operators. PABX is technically the only version used today, but we call it PBX for short.
Modern PBX systems include features like:
This is what people are referring to when they say PBX — no one is actually talking about manual switchboard operators.
Some businesses still use PBX systems connected to the PSTN, although many of them are in the process of switching to internet-based communications like VoIP. To make things even more confusing, you can technically also use VoIP on top of a PBX system.
Despite VoIP being the stronger choice for most, legacy phone systems do offer a few advantages:
However, they aren’t without their shortcomings.
Physical hardware makes them a real pain and expense to maintain and operate. When there are issues, you’ll likely have to call in a technician, which means possible downtime. And it gets even more complicated if you want to employ a remote workforce.
VoIP turns your voice into data packets and sends them over the internet to the person you’re calling. When the data packets arrive at their destination, they’re unpacked and converted back into sound.
Compared to the legacy phone systems I talked about above, VoIP is cheaper and far more flexible. You and your team can use it on any device connected to the internet, including your computer, mobile phone, or IP-enabled desk phones.
On top of that, VoIP services often include additional business features like call forwarding, advanced analytics, text messaging, voicemail-to-email, video conferencing, and more.
Perhaps the best part, though, is that you can administer your entire system from a computer. No hardware, control rooms, switch boards, or wires are needed.
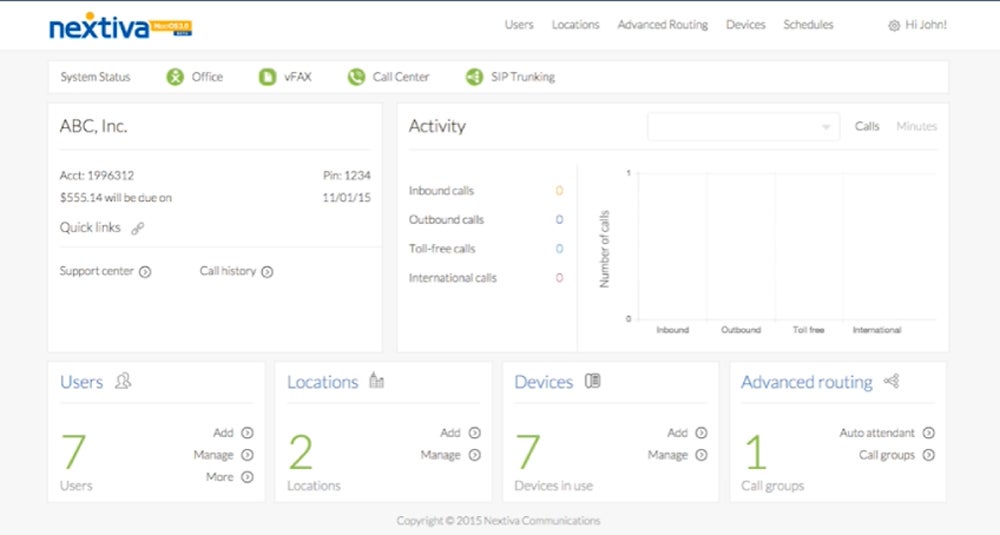
In terms of ease of use, Nextiva is one of the best. Inside the dashboard, you can easily configure and customize your phone system, adjust call routing flows, configure voicemail settings, and add new user extensions with just a few clicks.
When you see terms like cloud PBX or IP PBX, these are VoIP solutions.
They offer all the features you’d expect from a traditional PBX system (and more) but facilitate calls over the internet rather than through a physical infrastructure.
The only difference between cloud PBX and IP PBX is where they’re deployed. Cloud, or hosted, PBX refers to a system that’s maintained, secured, and updated by your provider. All of the software that runs your phone system is housed on their servers.
With IP PBX, it’s deployed on servers you own instead.
To recap, VoIP, cloud PBX, and IP PBX are all modern day phone systems with very few differences between them. PBX and legacy PBX typically refer to a legacy phone system that still uses physical wires and infrastructure rather than software stored on a server.
When comparing VoIP to traditional PBX systems, it becomes clear that VoIP offers several significant advantages that modern businesses can’t ignore.
VoIP involves lower set-up and operational costs than traditional PBX. It removes the need for expensive hardware, implementation, maintenance, and long-distance charges.
With traditional PBX, you’ll need a steady power supply, a huge switchboard and cabinet, phone lines, and other hardware to make the system function. That alone can easily cost several thousand dollars, if not more.
VoIP, on the other hand, requires very little hardware (if any). You can choose to purchase IP phones and headsets, but you don’t have to.
The only other cost you may need to consider is upgrading your internet.
The best VoIP phone services are highly scalable, letting you add or remove users with a few clicks from your computer. You likely don’t even need an experienced IT person to make these changes.
With traditional PBX, scaling up requires significant hardware investments. You’ll need to add more phone lines and set up new hardware as your business grows.
VoIP empowers remote work by allowing team members to make and receive calls from anywhere with an internet connection. Your team can handle calls from their computer or existing smartphone, meaning they can work from anywhere.
Traditional PBX systems tie businesses to central offices because of the hardware and physical connections required.
VoIP phone systems offer many advanced features, including voicemail-to-email, call forwarding, video conferencing, IVR, texting, conference calling, team chat, call recording, and more.
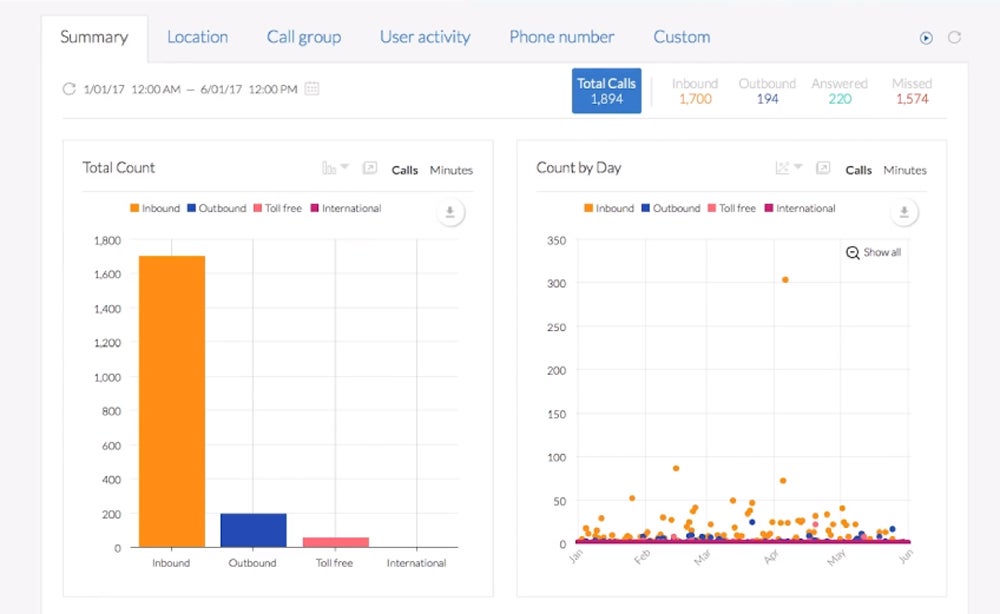
Many VoIP software solutions also offer built-in analytics, giving you all the data you need to make better decisions.
Because of the range of built-in collaboration features, many businesses can get rid of external team chat, video conferencing, audio conferencing, and text messaging solutions.
Traditional PBX systems won’t give you the same luxury — you’ll get a few basic features, and that’s it.
VoIP providers handle high-level remote monitoring and real-time security alerts at a minimum. They have a lot to gain by securing and maintaining their data centers, including the software housed in them.
Furthermore, most VoIP systems use strong encryption protocols to protect voice data as it travels over the internet. Beyond that, they’re often secured with intrusion detection and custom firewalls to protect against external threats and unauthorized access.
With traditional PBX systems, you’re on the hook for securing your own system.
Most VoIP providers offer one-click integrations with other software — your CRM software, customer service software, and ERP systems, to name a few.
Say a rep from your team receives a call from a customer. The system will automatically pull that customer’s data if it’s connected to your CRM. This enables your agents to offer more personalized customer experiences.
Software integrations consolidate data from different communication channels into a single platform, making it easier to manage and analyze. This provides valuable insights into customer behavior, call patterns, and performance metrics.
VoIP providers have multiple data centers in different regions for redundancy. In the event of an outage or unexpected failure at one center, traffic can be redirected to another. This, in turn, minimizes downtime to keep your system running.
The biggest issue businesses have with VoIP is due to their own internet. When stability or bandwidth issues happen with your network, it’s not uncommon to experience delays, echoes, and dropped calls.
That being said, VoIP systems tend to be far more reliable than PBX.
Additionally, PBX issues are notoriously hard to troubleshoot and fix. If you don’t have an experienced IT department to help, you may need to call in a technician. Every minute you wait for them to arrive, troubleshoot, and resolve your problems, your entire system is down.
If you’re considering VoIP but your company already has existing phone lines, you don’t have to throw your investment in the garbage.
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) gateways act as a bridge between analog PBX systems and VoIP software. Adding SIP can help you begin migrating to VoIP, reduce costs, and give your team new features while continuing to utilize your existing system.
SIP trunking makes it easier to match your system to the number of lines you need — you can easily add more without adding physical phone lines.
So, you can scale at a fraction of the cost while saving on long-distance and international calls.