Review your recent Gmail access, browser sign-in history and Google account activity to make sure no one other than you has used your account.
Whenever a computer is out of your direct view and control, there’s always a chance that someone other than you can gain access. A person who returns from a trip might wonder if their computer and accounts have been accessed during their absence. A person might notice odd activity in Gmail, not aware that their password has been made public (or “pwned“). Or, in some cases, a person might be surveilled by a partner, a family member, a colleague or even an unknown party.
SEE: Discover how to regain access to your Google account
To secure an account, you might first change your password, enable two-factor authentication or even enroll in Google’s Advanced Protection Program. Those steps will help you secure your account.
The following steps can help you figure out if someone other than you is accessing your Gmail or Google account.
Jump to:
In a desktop web browser, Gmail allows you to review recent email access activity. Select Details in the lower-right area below displayed emails, below Last Account Activity (Figure A).
Figure A

If your Gmail account has been accessed in other locations or on other devices, you may display recent activity while signed in to Gmail from a desktop-class web browser.
The system will show you information about the last 10 times your Gmail account has been accessed, along with the access type (browser, POP, mobile), location (IP address), and the date and time of access. This can help you identify if any of this access is from an unexpected device, place or time.
Note: If you use a virtual private network or a hosted desktop, the location data may reflect information related to your service provider, instead of your physical address.
In a few cases, I’ve had clients concerned about access in an expected location, but at an unexpected time. Sometimes, this was simply because they’d left a computer on, with their browser or mail client open. The system could be configured to auto-check mail periodically. In one case, access occurred after a power outage. They’d configure the system to automatically power on after an outage, so it signed in and downloaded new mail shortly after power was restored.
In the Chrome browser — and on any Chromebook or Chrome OS device — press Ctrl + H to display browser history. Alternatively, type chrome://history in the omnibox, or select the three-vertical dot menu in the upper-right, then choose History | History. On macOS, press Command + Y. You may scroll through all available sites visited. Review these to see if any sites displayed are unexpected.
SEE: Lock down your Google account on iOS with Google Smart Lock
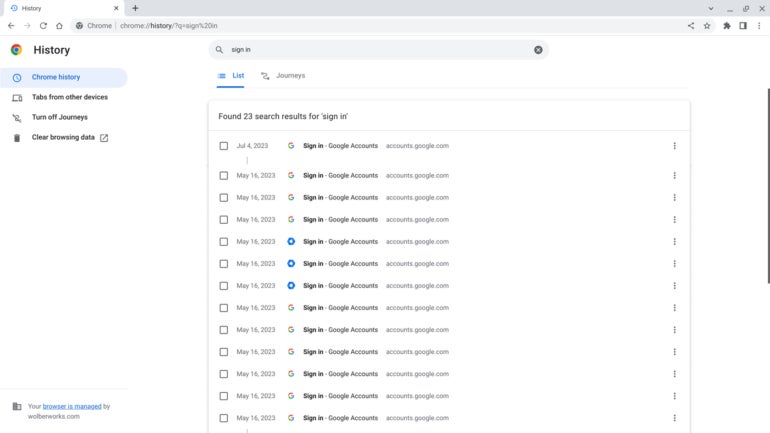
Additionally, you may enter search terms in the box displayed above the historical URLs listed. For example, search for “sign in,” or copy and paste this link into your browser omnibox: chrome://history/?q=sign%20in to display most site login pages (Figure B). Again, review the results for any sites you don’t expect. You might search for “gmail.com” as well.
Figure B
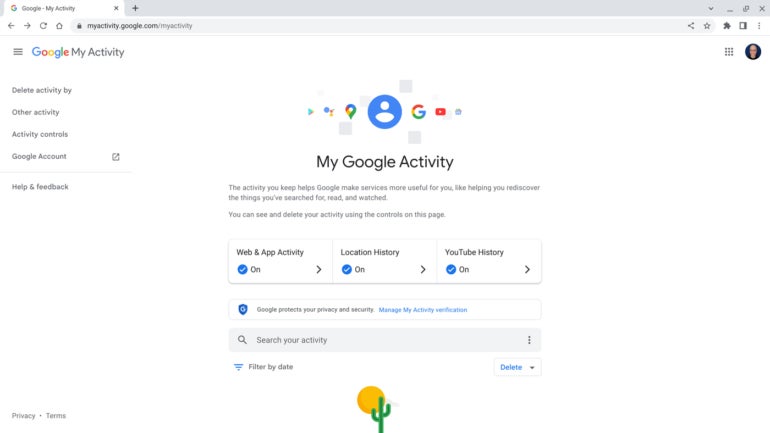
Go to https://myactivity.google.com/ to access your Google account history across all devices and Google services, such as YouTube, Google Maps and Google Play (Figure C). Depending on your security settings, you may need to reauthenticate when you attempt to access this information. Again, review any recorded data to make sure it corresponds with your usage.
Figure C
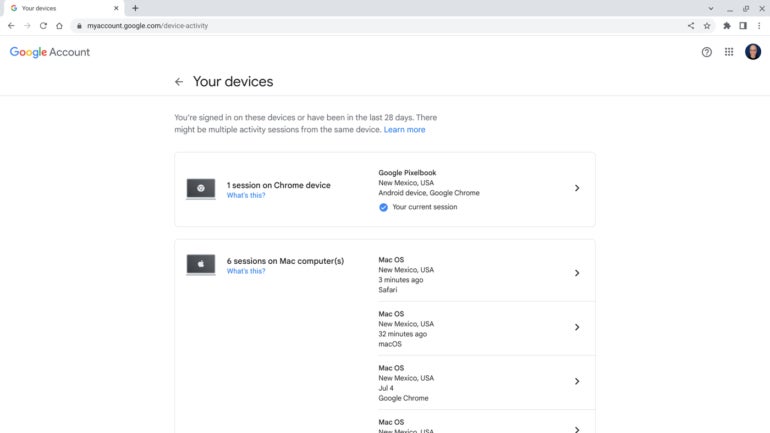
Similarly, go to https://myaccount.google.com/device-activity to review a list of devices to which you’ve signed in with your Google account (Figure D). You may select the arrow to the right of any displayed device session, then choose Sign Out to prevent any future access without reauthentication on a device.
Figure D
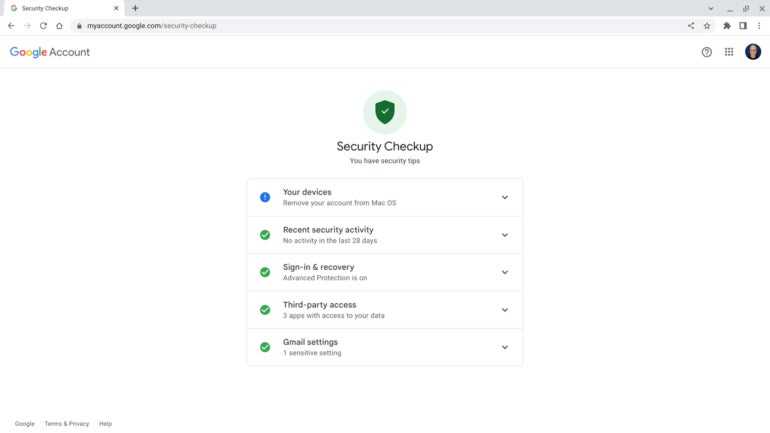
Go through Google’s Security Checkup for a step-by-step review of every item Google’s system identifies as a potential security issue (Figure E).
Figure E
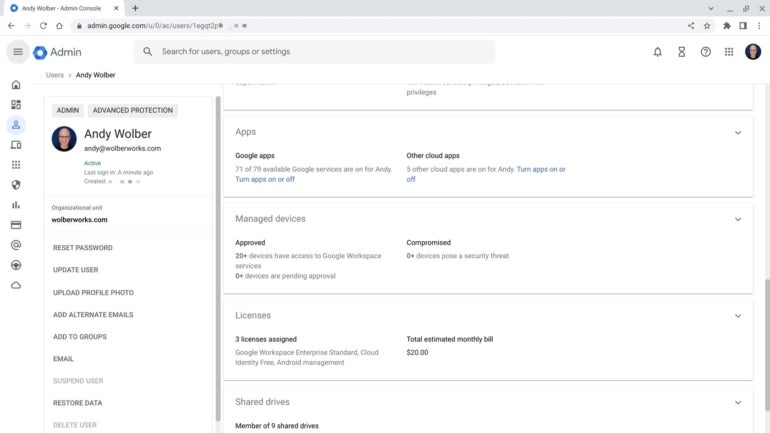
If you use Gmail and Google Workspace as part of an organization (e.g., work or school), an administrator may be able to do an additional review of your account access data. To do this, the administrator will need to sign in to the admin console. From the Admin console, they might go to https://admin.google.com/ac/, select your account, then review security settings as well as connected apps and devices (Figure F).
Figure F
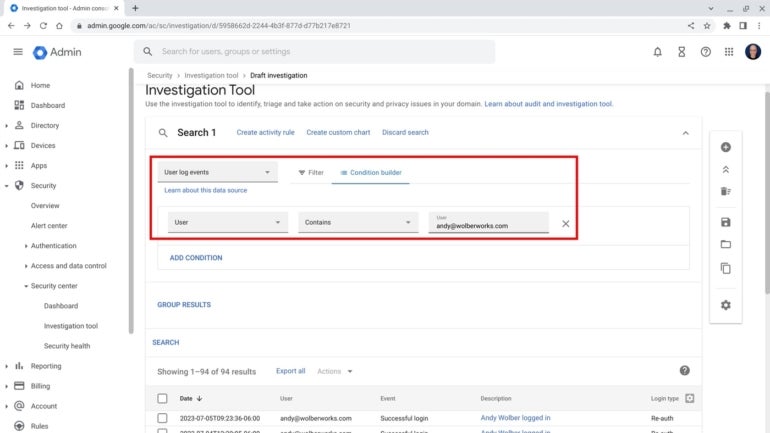
Next, admins might review all login information by going to the Investigation Tool, then filtering by user log events and your account email address (Figure G). Because this information is centrally logged by the system, access records will remain, even if the person accessing your account attempts to cover their tracks, such as by locally deleting browser history.
Figure G
If you’ve wondered whether someone else has accessed your Google account, what steps have you taken? What did you learn when you completed the above access review of your Google account? Mention or message me on Mastodon (@awolber) to let me know any additional steps you suggest.