This is a comparison of Duo and Microsoft Authenticator. Learn more about their key differences, features, security, and performance in this in-depth analysis.
Two-factor authentication, which is a form of multi-factor authentication, has emerged as a crucial security measure for organizations to enhance the security of their users. Duo and Microsoft Authenticator are two popular apps that provide this level of security.
Duo uses push notifications, time-based, one-time passwords, physical tokens and biometrics to verify the identity of users at login. Similarly, Microsoft Authenticator uses push notifications, one-time passcodes, and biometrics for authentication and can integrate with Microsoft 365 and Azure Active Directory. While both 2FA options share some similarities, there are still key differences that can sway your decision to choose one over the other.
| Features | Duo | Microsoft Authenticator |
|---|---|---|
| Push notifications | Yes | Yes |
| Biometrics authentication | Yes | Yes |
| One-time passcodes | Yes | Yes |
| Integrations with other products and services | Very wide | Microsoft-first and limited |
| Backup and recovery | Yes | Yes |
| Pricing | Comes with a free trial and starts at $3 per user, per month. | Offers a free version but comes bundled with Microsoft Azure Active Directory and 365 Business accounts |
Below is how Duo and Microsoft Authenticator square up against each other in terms of pricing.
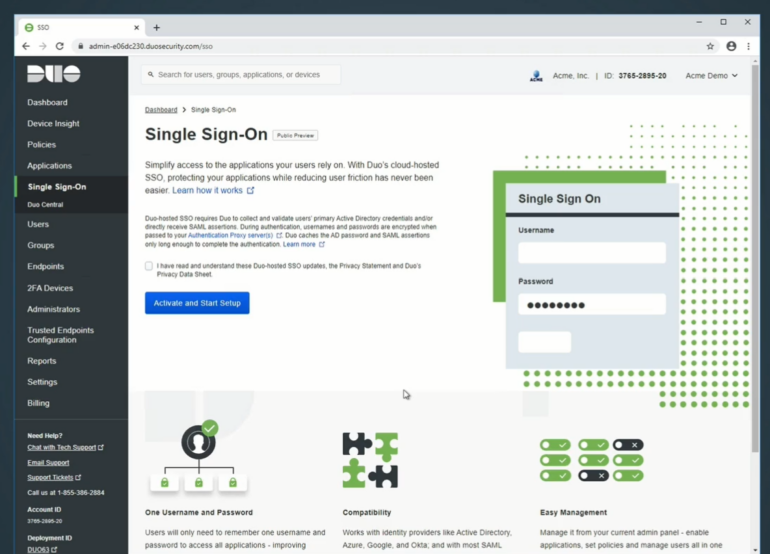
Duo follows a tiered system based on features and services you would like added to the application.
Figure A
Microsoft Authenticator pricing follows a straightforward model of being free and bundled with all Microsoft Azure Active Directory and 365 Business accounts. For a full list of prices and features, visit this guide to determine if Microsoft Authenticator is bundled with your organization’s existing licenses.
Both Duo and Microsoft Authenticator present excellent features to users but here is a head-to-head feature comparison:
Most enterprise organizations considering Duo or Microsoft Authenticator will want to integrate these apps with existing software or custom software and server applications. Duo supports unlimited application integrations through its platform on all editions available. On the other hand, while Microsoft Authenticator also integrates with other third-party products and services, it is far easier to integrate with Microsoft-supported services because it’s already bundled with some of them.
Both Duo and Microsoft Authenticator prioritize security and offer robust features to protect user accounts. Duo supports adaptive authentication, which assesses the risk of each login attempt and prompts for additional verification when necessary. It also provides granular access policies, allowing administrators to define specific authentication requirements based on user roles and conditions. Microsoft Authenticator leverages the power of Azure Active Directory to deliver advanced security features such as conditional access policies, risk-based authentication, and seamless single sign-on experiences across applications. It also supports hardware-backed security keys for enhanced protection against phishing attacks.
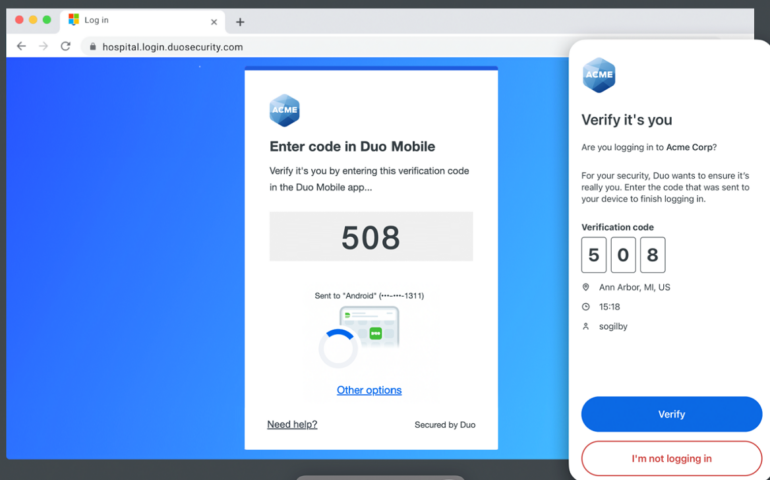
Both Duo and Microsoft Authenticator provide multiple authentication methods. Duo offers a variety of authentication options, including push notifications, one-time passcodes (OTPs), phone calls, and hardware tokens. Microsoft Authenticator also supports push notifications, OTPs, and biometric authentication (fingerprint, facial recognition) on supported devices. (Figure B)
Figure B

Duo provides options for the backup and recovery of authentication devices. Users can enroll multiple devices as backups, ensuring access to their accounts even if their primary device is lost or unavailable. This feature adds an extra layer of convenience and ensures continuity of access. Microsoft Authenticator also offers backup and recovery options, allowing users to securely store their accounts and settings in the cloud. This feature enables easy restoration of accounts on new devices or in case of device loss. (Figure C)
Figure C
While Duo presents many benefits to users, it also leaves some drawbacks. Here is a summary of the pros and cons.
Microsoft authenticator offers powerful two-factor authentication features, but there may be a few drawbacks some users say they have experienced while using the product. Below are some of the pros and cons.
In order to draw a fair comparison between Duo and Microsoft Authenticator, we started by going through the documentation pages of each product, where we learned about their key features and how they integrate with other technologies. We also checked out user reviews from trusted third-party review sites to fetch some opinions from verified users. The writer also uses Microsoft Authenticator, making it easier to discuss the product based on my experience. All these provided enough insight that helped in shaping our review.
Picking one 2FA software over another can be challenging, especially when many striking similarities bind the products together. For Duo and Microsoft Authenticator, the main point of reference when you have to decide to pick between the two should revolve around your overall technology stack, ease of use and pricing.
If you heavily rely on Microsoft products such as Azure Active Directory, Microsoft 365, and other Microsoft services, Microsoft Authenticator may provide a more seamless and integrated experience. On the other hand, if you have a diverse set of platforms and applications, Duo’s broad compatibility and extensive integration capabilities make it a more versatile choice. Duo integrates easily with services like Slack, Atlassian, Salesforce, Dropbox and more.
You should also consider the pricing models and how they meet your business requirements and budgets. Duo’s pricing structure varies depending on the features and support level chosen, while Microsoft Authenticator is typically bundled with Azure Active Directory and Microsoft 365 subscriptions. Duo’s pricing is more comprehensive and transparent, unlike Microsoft’s, which is more complicated due to its bundling with Azure Directory and Microsoft 365 subscriptions. So, it’s important to evaluate your organization’s specific needs and consider the associated costs when comparing the pricing of these solutions.
Also, consider the user experience and ease of use. Evaluate the authentication methods each solution offers and their compatibility with your users’ devices. Both Duo and Microsoft Authenticator provide seamless user experiences, but preferences may vary depending on your organization’s tech stack, user base and how familiar they are with each platform. You can use the free versions offered by each solution to determine which provides the best user experience for your company. The free tier could help you assess things such as the simplicity of setup, the intuitiveness of the authentication process, and any additional features that enhance usability.
Finally, the decision between Duo and Microsoft Authenticator will depend on your organization’s unique needs, infrastructure, and priorities. Consider conducting a pilot test with both solutions to evaluate their performance and compatibility within your business environment. This will allow you to gather firsthand experience and feedback from your users and administrators before making a final decision.
For a more comprehensive evaluation of two-factor authentication based on security impact and strategic business initiative, check out this two-factor authentication evaluation guide.
Read next: Two-factor authentication: A cheat sheet